 Image credit: ACS
Image credit: ACSAbstract
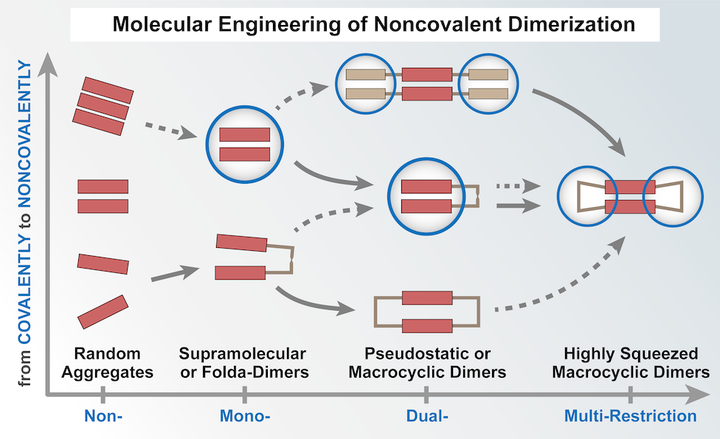
Dimers are probably the simplest model to facilitate the understanding of fundamental physical and chemical processes that take place in much-expanded systems like aggregates, crystals, and other solid states. The molecular interplay within a dimer differentiates it from the corresponding monomeric state and determines its features. Molecular engineering of noncovalent dimerization through applied supramolecular restrictions enables additional control over molecular interplay, particularly over its dynamic aspect. This Perspective introduces the recent effort that has been made in the molecular engineering of noncovalent dimerization, including supramolecular dimers, folda-dimers, and macrocyclic dimers. It showcases how the variation in supramolecular restrictions endows molecular-based materials with improved performance and/or functions like enhanced emission, room-temperature phosphorescence, and effective catalysis. We particularly discuss pseudostatic dimers that can sustain molecular interplay for a long period of time, yet are still flexible enough to adapt to variations. The pseudostatic feature allows for active species to decay along an alternate pathway, thereby spinning off emerging features that are not readily accessible from conventional dynamic systems.