On-resin Recognition of aromatic Oligopeptides and Proteins through host-enhanced Heterodimerization
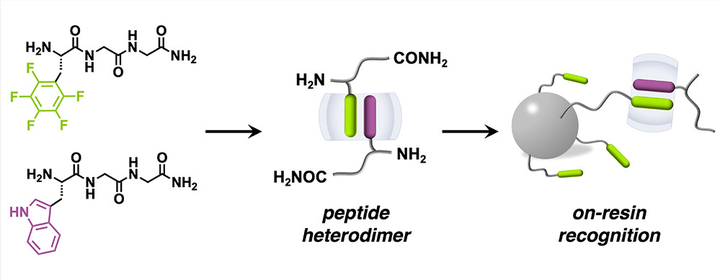 Image credit: ACS
Image credit: ACS摘要
Peptide dimerization is ubiquitous in natural protein conjugates and artificial self-assemblies. A major challenge in artificial systems remains achieving quantitative peptide heterodimerization, critical for next-generation biomolecular purification and formulation of therapeutics. Here, we employ a synthetic host to simultaneously encapsulate an aromatic and a noncanonical l-perfluorophenylalanine-containing peptide through embedded polar−π interactions, constructing an unprecedented series of heteropeptide dimers. To demonstrate the utility, this heteropeptide dimerization strategy was applied toward on-resin recognition of N-terminal aromatic residues in peptides as well as insulin, both exhibiting high recycling efficiency (>95%). This research unveils a generic approach to exploit quantitative heteropeptide dimers for the design of supramolecular (bio)systems.