Applying support-vector machine learning algorithms toward predicting host–guest interactions with cucurbit[7]uril
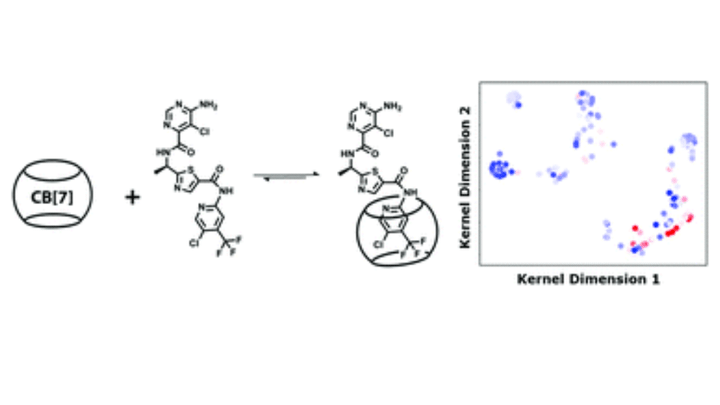 Image credit: RSC
Image credit: RSCAbstract
Machine learning is a valuable tool in the development of chemical technologies but its applications into supramolecular chemistry have been limited. Here, the utility of kernel-based support vector machine learning using density functional theory calculations as training data is evaluated when used to predict equilibrium binding coefficients of small molecules with cucurbit[7]uril (CB[7]). We find that utilising SVMs may confer some predictive ability. This algorithm was then used to predict the binding of drugs TAK-580 and selumetinib. The algorithm did predict strong binding for TAK-580 and poor binding for selumetinib, and these results were experimentally validated. It was discovered that the larger homologue cucurbit[8]uril (CB[8]) is partial to selumetinib, suggesting an opportunity for tunable release by introducing different concentrations of CB[7] or CB[8] into a hydrogel depot. We qualitatively demonstrated that these drugs may have utility in combination against gliomas. Finally, mass transfer simulations show CB[7] can independently tune the release of TAK-580 without affecting selumetinib. This work gives specific evidence that a machine learning approach to recognition of small molecules by macrocycles has merit and reinforces the view that machine learning may prove valuable in the development of drug delivery systems and supramolecular chemistry more broadly.